Price List
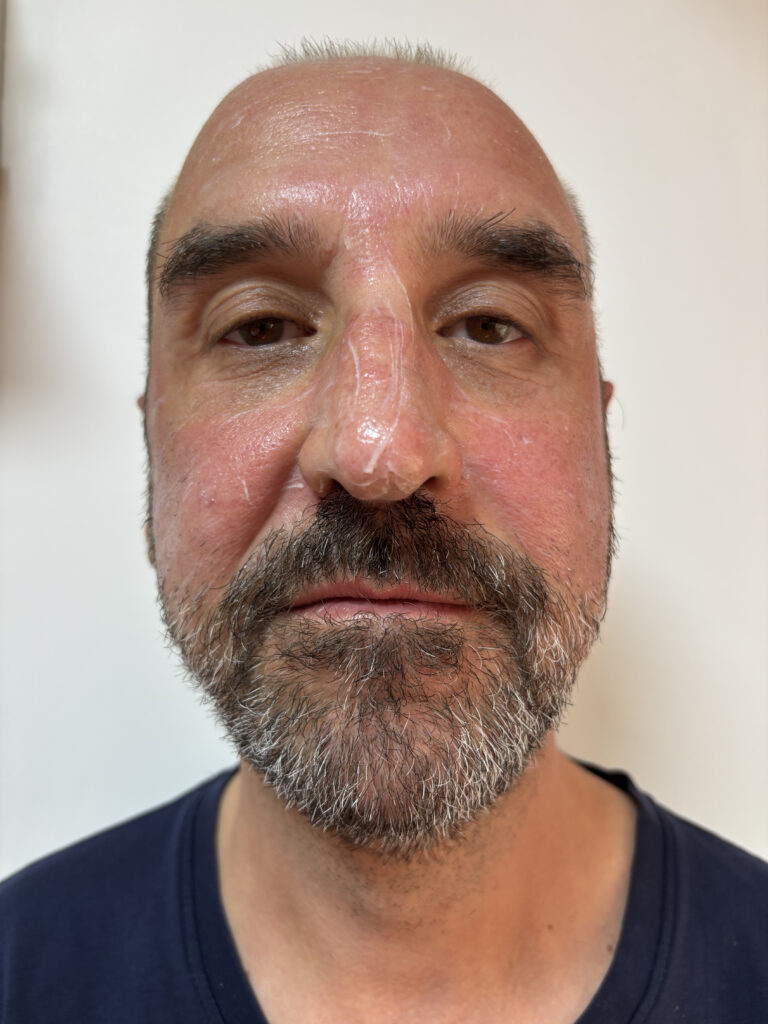



Aftercare:
Rest the treated area: After the procedure, avoid strenuous physical activity for at least 48-72 hours to allow the body to heal effectively.
Ice application: Applying ice to the treated area for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce swelling and discomfort.
Avoid direct sunlight: After PRP facial rejuvenation treatments, protect the skin from direct sunlight and use a high SPF sunscreen to avoid pigmentation issues.
Pain management: Mild discomfort or soreness may occur at the injection site. Over-the-counter pain relief (like ibuprofen or paracetamol) can help manage pain, but always follow the practitioner’s advice.
Hydration: It’s important to stay well-hydrated after treatment to support the healing process.
Monitor for side effects: While rare, complications like infection, prolonged swelling, or excessive pain may require medical attention.
Follow-up appointments: Depending on the condition being treated, follow-up appointments are often scheduled to assess progress and determine if additional treatments are needed.