Price List
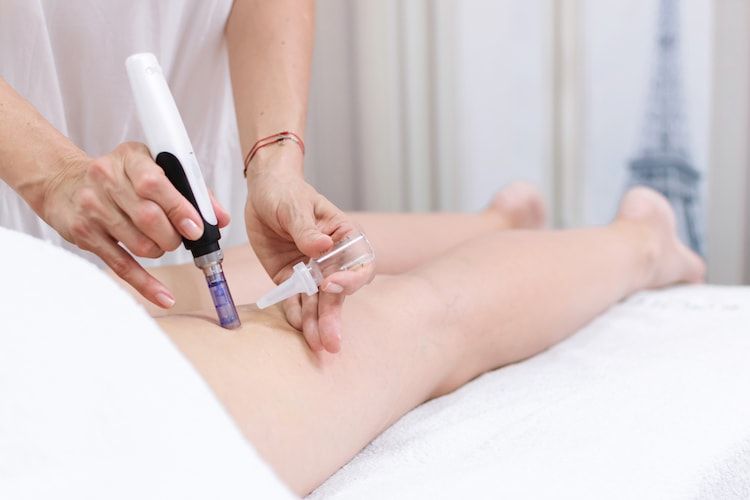



Aftercare:
Avoid sun exposure: After microneedling, the skin is more sensitive and prone to sun damage. Avoid direct sun exposure for at least 24-48 hours, and use a broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) daily.
Avoid makeup: It is advisable to avoid wearing makeup for at least 24 hours post-treatment, as the skin may be more vulnerable to irritation or infection.
Gentle cleansing: Use a mild, non-abrasive cleanser to gently wash the treated area. Avoid using exfoliants, scrubs, or strong chemical treatments for several days.
Hydration: Hydrate the skin well after the procedure using a hydrating serum or moisturizer. Hydrating agents like hyaluronic acid are commonly applied to the skin after microneedling to lock in moisture and aid recovery.
Avoid heat and sweating: Refrain from hot showers, saunas, or heavy exercise for 24-48 hours after the treatment to prevent irritation or excessive sweating that could interfere with healing.
Avoid touching or picking at the skin: Refrain from touching the treated area with unclean hands and avoid picking or scratching, as this can lead to infection or scarring.
Apply soothing creams or serums: Your practitioner may recommend using specific soothing serums or creams (such as hyaluronic acid, growth factors, or vitamin C) to help reduce redness and inflammation, and promote healing.
Redness and swelling: Mild redness, swelling, or tightness in the treated area is normal and typically subsides within a few hours to a couple of days. If swelling persists or there is increased pain, contact your practitioner.
Avoid certain skincare treatments: Do not use retinoids, alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), or beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) for at least 5-7 days following treatment, as they can cause irritation.
Avoid swimming: Avoid swimming in chlorinated pools or saltwater for about a week to reduce the risk of infection.